Oracle Sub Ledger Accounting (SLA) r12 Summary
Compiled By:Prasanna Kumar Reka
Oracle Applications Consultant
rekaapps@yahoo.com
Topics:
1. SLA is a new product
2. Inconsistent Accounting Practices in earlier releases
3. Centralized repository for Sub-Ledger Accounting with Multiple Accounting Representations Support
4. Flexible Accounting Definitions
5. Draft Accounting
6. Online Accounting
7. Replacement for Disabled accounting
8. On-Line inquiries
9. Journal Entry Sequencing
10. Sub-ledger Manual Journal Entries
11. Multi-Period Accounting
12. Standard Reports with XML Publisher Template
13. Diagnostics framework
14. Other Enhancements
SLA is a new product• Sub-Ledger Accounting is new product in release 12, users will not find this as a separate module, infact they are provided as extra functions with in Sub-Ledgers
• Sub-Ledger is designed leveraging the Common Accounting Module (XLA), Global Accounting Engine (AX) and event based accounting model introduced earlier in accounting for AP transactions.
Inconsistent Accounting Practices in earlier releases• There are lot of inconsistencies in accounting in earlier releases:
-->AP-creates and stores accounting in AP and then transferred to GL
-->AR- no dr/cr are created and stored in AR but distribution information is transferred to GL to create accounting
-->FA- Creates directly into General Ledger
-->PA-Accounting created for 2 sides dr/cr differently
• Sub-Ledger addresses this issue and accounting from all sub-ledgers (complete dr/crs) are stored in sub-ledger first then transferred to General Ledger
Centralized repository for Sub-Ledger Accounting with Multiple Accounting Representations Support• Now Sub-ledger serves as a centralized repository or common source for all sub-ledger accounting data. Provides the complete links and references between GL financial information and source transactions in Sub-Ledgers. New tables introduces for storing sub-ledger transactions which start with XLA_. Tables used to store Accounting Events, Reconciliation references and accounting information.
• Sub-Ledger facilitates Multiple accounting Representations (MAR) which facilitate posting accounting from a single source to different ledgers in different ways as designed (Accounting Methods).
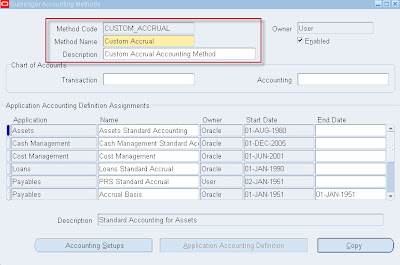
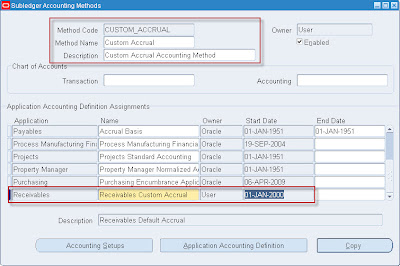
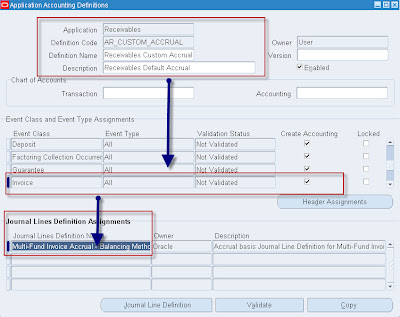
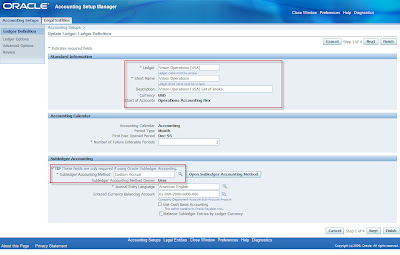
Flexible Accounting Definitions• Setting up of Accounting Methods are critical setup for Sub-Ledger accounting. Users can copy seeded accounting methods and change wherever required instead of defining from the scratch.. User Type “Oracle” represents seeded accounting methods and “User” represents user created accounting methods.
• Sub-ledger Accounting Method (SAM)-->Application Accounting Definition (AAD)-->Journal Entry Setups-->Account Derivation Rules (ADR)
•
Accounting Setups:
• Sub-Ledger Accounting Method (SAM) --> Ledger Level grouping which is a superset of all Application accounting Definitions (AAD)
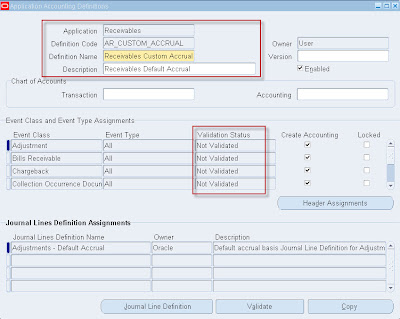
• Application Accounting Definition (AAD)--> Sub-ledger or Application level (ex: AP,AR) grouping which is superset of all Journal Entry Definitions. AADs can be created with date effective, which facilitate creation of multiple AADs for each application with different date ranges.
• Journal Entry Setups: Which is critical setup for definition GL date, descriptions, reconciliation references and account derivation rules for generating journal entries for sub-ledger transactions.
• Account Derivation rules are part of Journal Entry setups which derive separate segments to form GL code combination or complete GL code combination. “Conditions” can be used to determine how and when many of these components are used and to create defaults
Draft Accounting
Two accounting generation modes are provided in SLA 1) Final 2) Draft. By creating accounting in DRAFT mode users can check the accounting entries before they are being transferred to GL as final accounting. User can regenerate the accounting again in DRAFT till they are satisfied, process can be repeated any number of times. This minimizes the need for correcting the JEs in general Ledger and facilitates a clean audit as review and corrections are completed in SLA. Accounting created in DRAFT mode is not transferred to General Ledger, DRAFT accounting is for review only purposed and stored in SLA.
Once transactions are reviewed and satisfied accounting is created in “FINAL” mode and final accounting is transferred to GL. Users can create accounting as “FINAL” without actually using “DRAFT” mode of generating accounting. Accounting modes and mode override options are setup in Sub-Ledger options.
Online Accounting• Ability to immediately create, view, transfer and post accounting in GL when transactions are entered into sub-ledgers like AP (related setups are setup/selected in Sub-ledger setup options and while running concurrent programs).
• Common accounting rules and validations for both offline and online accounting
• Users can create accounting online in draft mode, view adjust before creating accounting in final mode.
Replacement for Disabled accounting
• When an account is disabled, users can continue to create accounting for transactions that include the disabled account without erroring. Oracle SLA stores substituted disabled account on SLA journal lines for audit and reconciliation purposes.
On-Line inquiriesSLA takes advantages of Oracle personalization framework that allows users to customize their view of the accounting using any of the attributes of the journal entry and to save predefined searches. Embedded flows support a bi-directional drill between journal entry headers, lines, T-Account and Transaction data.
Journal Entry Sequencing
Sequencing information is available for querying and display of journals. SLA provides two different sequence mechanisms for sub-ledger journal entries:
1) Accounting Sequence
2) Reporting Sequence
# Accounting Sequencing: SLA assigns a sequence to its journal entries as they are completed.
Reporting Sequencing: Designed to meet legal requirements in southern Europe. Reporting sequence is assigned to both the sub-ledger and general ledger journals entries when the GL period is closed.
Reporting sequence feature replaces the accounting Engine (AX) legal sequencing and Libro Giornale fetures. This type of sequence is used by the most of the legal reports required in some countries as the main sorting criteria to display the journal entries.
Sub-ledger Manual Journal EntriesNew Sub-Ledger manual Journal Entries can be created with in the context of the application. There is no concept of Manual JEs in previous releases except for GL.
Multi-Period Accounting
Users can create accrual and recognition journals to allocate costs over a range of accounting periods. Users can also configure GL Date,a prorating method and have the ability to create a single recognition journal based upon the multi period end date.
Recognition journal for the future periods are created as incomplete until the period is open or enterable and are available for inquiries and reports.
Standard Reports with XML Publisher Template
Some critical reports are:
• Journal Entries Report
• Accounting Analysis Report
• Third Party Balances Report
• Open Account balances listing
• Sub –Ledger period close exception report
Diagnostics framework• Provide a tool to view the information used to create sub-ledger journal entries.
• Helps in understanding how the Journal Entry Setups were used to create journals
• Results of the diagnostics are available as an HTML Report
Other Enhancements• Ability to account for changes for Third Parties
• Automatic reversal of Accrual entries either next day or into next accounting period
• Accounting policies based on intra or inter-product business flows
• SLA replaced Global Accounting Engine (AX)
• Ability to calculate gain/loss for foreign currency transactions in SLA and use ADRs to account for gain/loss in flexible way.
• Journals created with errors are not transferred to GL, users can view the error journals online or using standard XML publisher. Once corrected user can re-create the accounting. Ex: Journals created for closed GL period.
• AAD loader enables export and import of accounting definitions and journal entry setups. Users can test the Accountign definitions in test instance export and import them into production instance once duly tested.
• MRC functionality is enhanced to support all journal sources. Reporting SOB are now known simply as reporting currencies.
• Users can elect to account for a limited subset of their journals based upon business transaction entities using process categories.